Track mileage automatically
Get startedMileage allowance for the self-employed
As self-employed, you can claim mileage allowance from HMRC for the usage of your personal vehicle for business purposes. HMRC provides two methods through which you can claim self-employed car expenses. You can claim mileage at a flat per-mile rate, or claim all your actual business car expenses.
Never miss a trip. With the Driversnote mileage tracking app you have the tool to ensure every business-related mile you drive is properly logged and categorised.
Self-employed mileage rules
Before we get into how you can claim mileage and other car expenses, there are some general rules you should be aware of.
If you use a Trading Allowance
If you make use of the tax-free Trading Allowance, you will not be able to claim any allowable business expenses, including vehicle costs. If you want to know more about why you cannot claim other allowable costs, you can read HMRC’s article on Trading Allowance.
If you have a limited company
If you run your own limited company and use your private vehicle for work, you will be able to pay yourself Mileage Allowance Payments (MAPs) from your company and claim other business travel costs as allowable business expenses (e.g. parking fees, train fares, accommodation).
If your limited company owns the vehicle, you will only be able to claim Advisory Fuel Rates (AFR) set by HMRC and the company will take on the expenses of vehicle maintenance and other travel expenses.
If you also drive your vehicle for private purposes
If you use your vehicle for both private and business purposes, you will only be able to claim a self-employed mileage allowance for your business mileage. To accurately manage this, you will need to regularly record your total mileage - both for private and business trips.
You will also need to keep in mind HMRC’s rules on what is considered business travel:
- Travel between your permanent workplace and your temporary work
- Travelling between temporary workplaces
- Travel between two workplaces in the same employment
- Travelling from home to another workplace if “home” is your permanent workplace due to the requirements of the job.
One key thing to note - if you work from an office and not from your home, you can’t count commuting to and from work (your permanent workplace) as a business trip.
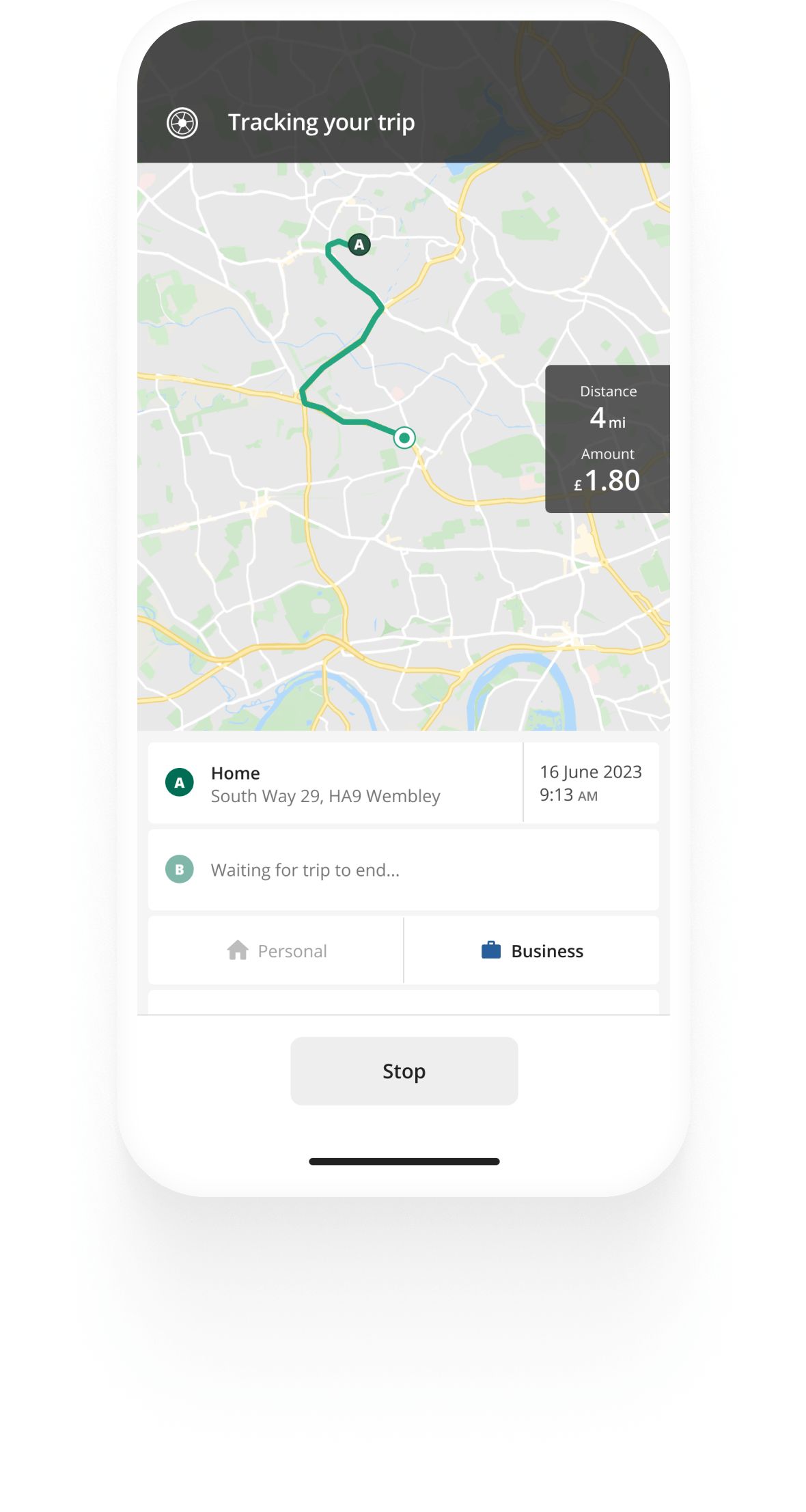

Mileage tracking made easy
Trusted by millions of drivers
Automate your mileage log Automate your mileage log
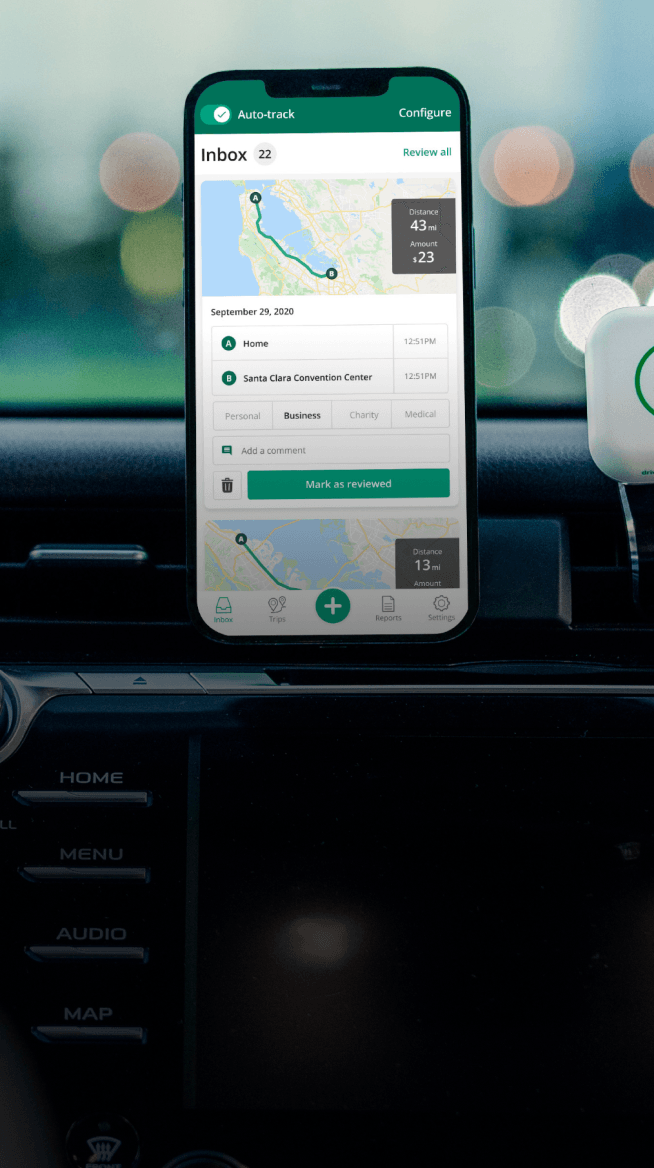
Automatic mileage tracking and HMRC-compliant reporting.
Get started for free Get started for freeSelf-employed mileage allowance
If you are self-employed, you have two ways to claim mileage allowance and other vehicle expenses for your business: using actual vehicle costs or simplified expenses (mileage rate).
You should carefully consider which one you want to use. Using actual vehicle costs is more time consuming but gives you the most accurate reading of your actual vehicle expenses. Using a mileage rate is a simpler solution, but may not properly reflect your actual vehicle costs.
If you are unsure of which method will suit you best, try out HMRC’s simplified expense checker. This tool will help you find the best solution for yourself and your business.
Mileage allowance with the actual vehicle expenses method
The first method you can use to claim mileage if you’re self-employed is to record all costs incurred from using your vehicle for business-related driving. At the end of the tax year, you will be able to deduct the costs from your company’s taxable profit.
This way of claiming vehicle costs might be better for you if your vehicle expenses are high due to high road tax, insurance, fuel consumption, etc. However, it is a more time-consuming way of recording your vehicle expenses.
The vehicle costs you can deduct include:
- Fuel
- Vehicle insurance
- Repairs and maintenance
- Servicing
- Breakdown cover
- Parking
- License fees
There are other allowable travel expenses you can claim besides your vehicle costs. These are accommodation and meal prices for business trips, journeys with other vehicles (e.g. train or airfares) and car hire charges.
If you are not sure what records you need to keep as self-employed, jump over to our article on self-employed mileage allowance records.
Mileage allowance with the simplified expenses method
The aptly-named simplified expenses method is great if you want to save time by not having to log every single vehicle expense. Instead, you calculate your vehicle expenses using a flat rate set by HMRC. The flat rate is meant to cover all vehicle costs, just like the standard mileage allowance; that would be fuel, servicing and repairs, maintenance, depreciation, and insurance and road tax.
Keep in mind you can’t use simplified expenses if you have claimed capital allowance for your vehicle or have included it in your business expenses.
Also, if you use the simplified expenses method for your vehicle, you can’t switch to actual vehicle costs as long as you still use that same vehicle for work. You can, however, switch from actual vehicle costs to simplified expenses.
You can see the approved mileage rates from HMRC in our article about 2025 HMRC mileage rates.
Other allowable expenses you can claim on top of the simplified expenses method are parking fees, journeys with other vehicles (e.g. train tickets), car hire charges, accommodation and meal prices for work-related trips.
FAQ
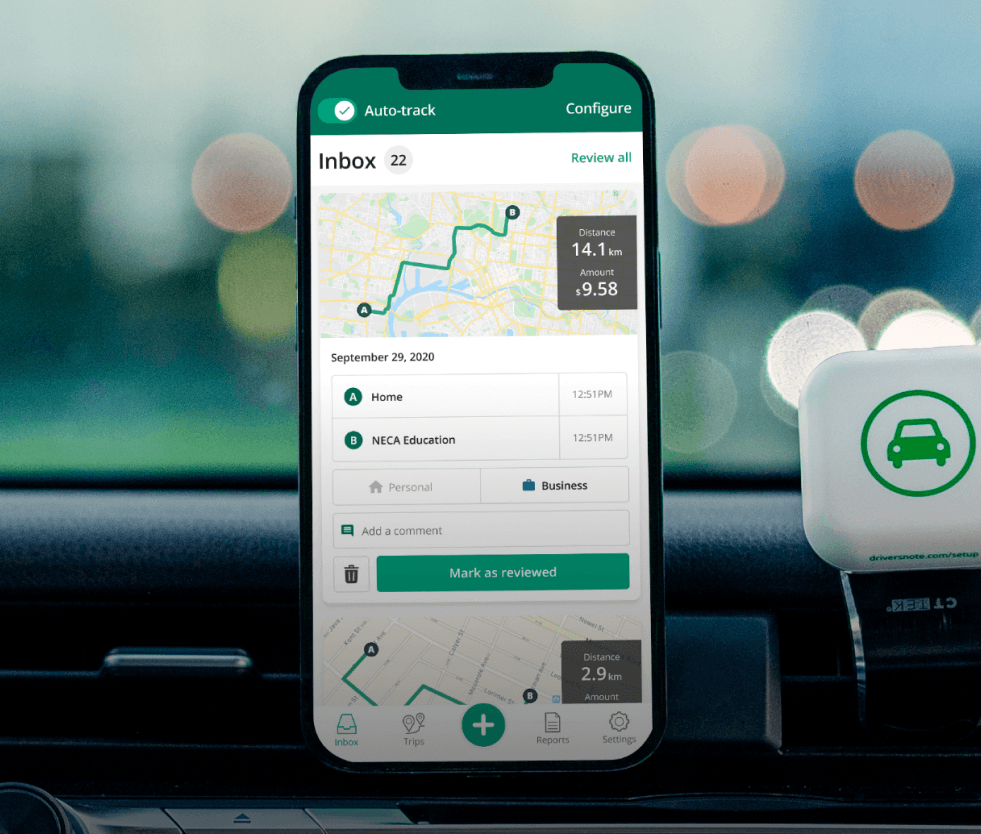
Tired of logging mileage by hand?
Effortless. HMRC-compliant. Liberating.
HMRC Mileage Guide
- For self-employed
- For employees
- HMRC mileage claim in 5 steps
- Self-employed mileage allowance records
- Car allowance for employees
- Salary sacrifice car scheme
- Mileage Allowance Relief
- HMRC mileage rate 2022
- HMRC mileage rates 2021