Track mileage automatically
Get startedHMRC Mileage Guide
Welcome to our guide on mileage claims and reimbursement in the United Kingdom. This guide will walk you through and help you understand the rules that apply to your situation for HMRC mileage claims.
Are you wondering if you did your vehicle log book properly? With Driversnote as your mile tracking app your trips are automatically logged with all the needed information, just the way the HMRC likes it.
What is a mileage claim?
Many employees and self-employed individuals drive their own cars for both personal and business purposes. Business-related driving with one’s personal vehicle grants reimbursement for the accrued mileage and the expenses that come with it. Furthermore, companies often compensate their employees tax-free for business costs incurred in personal vehicles. In most cases, the reimbursement is on a rate per mile basis and includes the cost of fuel and the cost of maintenance and repairs for the vehicle in question.
Vehicles eligible for HMRC mileage claim
HMRC’s rules surrounding mileage claims for business mileage allow for reimbursement for the following vehicles: cars, vans, motorcycles and bicycles.
Mileage that qualifies for reimbursement
It is simple - if your trip was for business purposes, then you are entitled to claiming mileage based on HMRC rules. What qualifies as a business trip according to HMRC:
- Travel between your permanent workplace and your temporary work (e.g. visiting clients or suppliers)
- Travelling between temporary workplaces
- Travel between two workplaces in the same employment
- Travelling from home to another workplace if “home” is your permanent workplace due to the requirements of the job.
What does not qualify as a business trip is commuting from your home to your workplace, or trips that are personal and clearly not for business purposes.
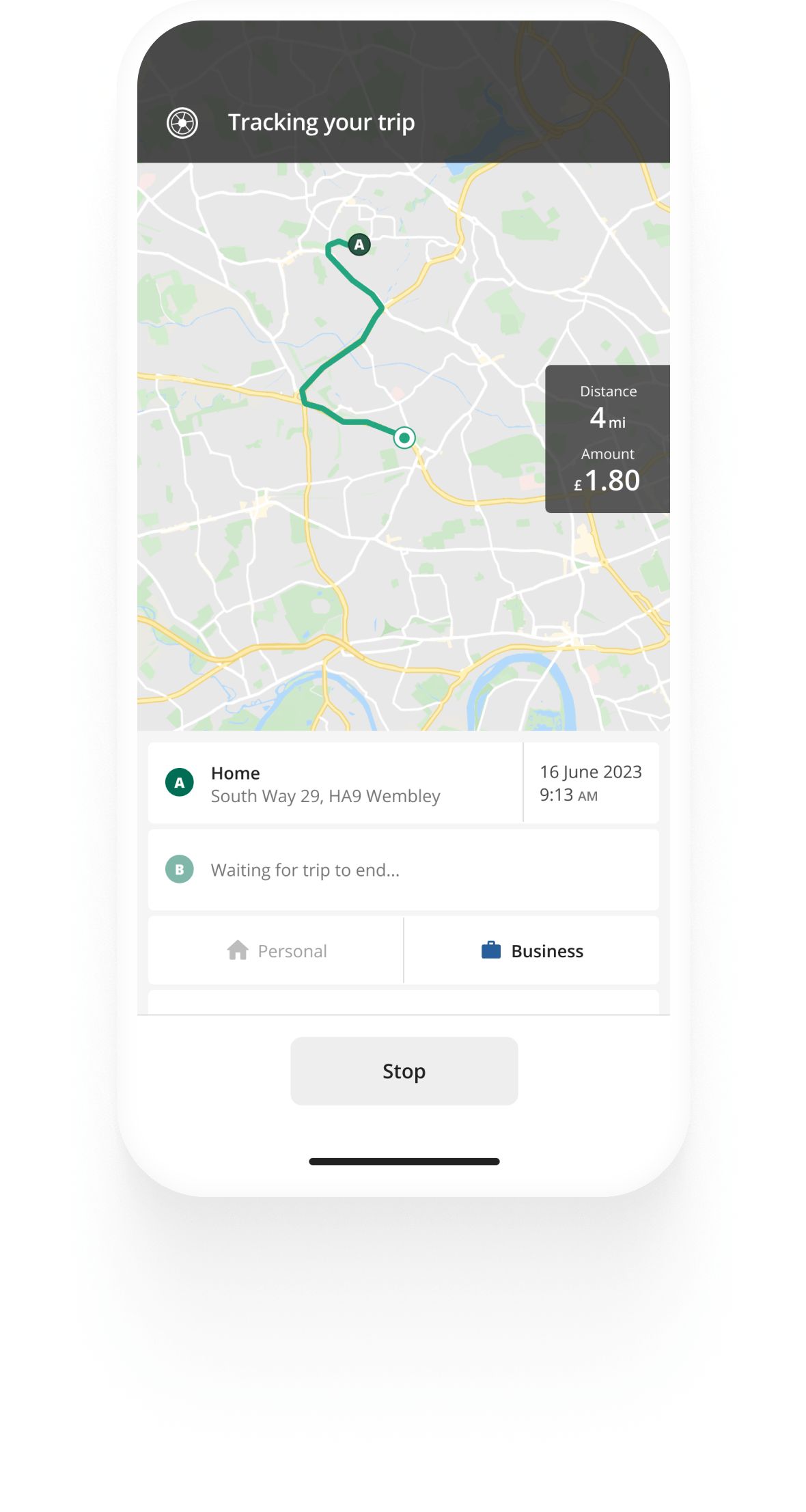

Mileage tracking made easy
Trusted by millions of drivers
Automate your mileage log Automate your mileage log
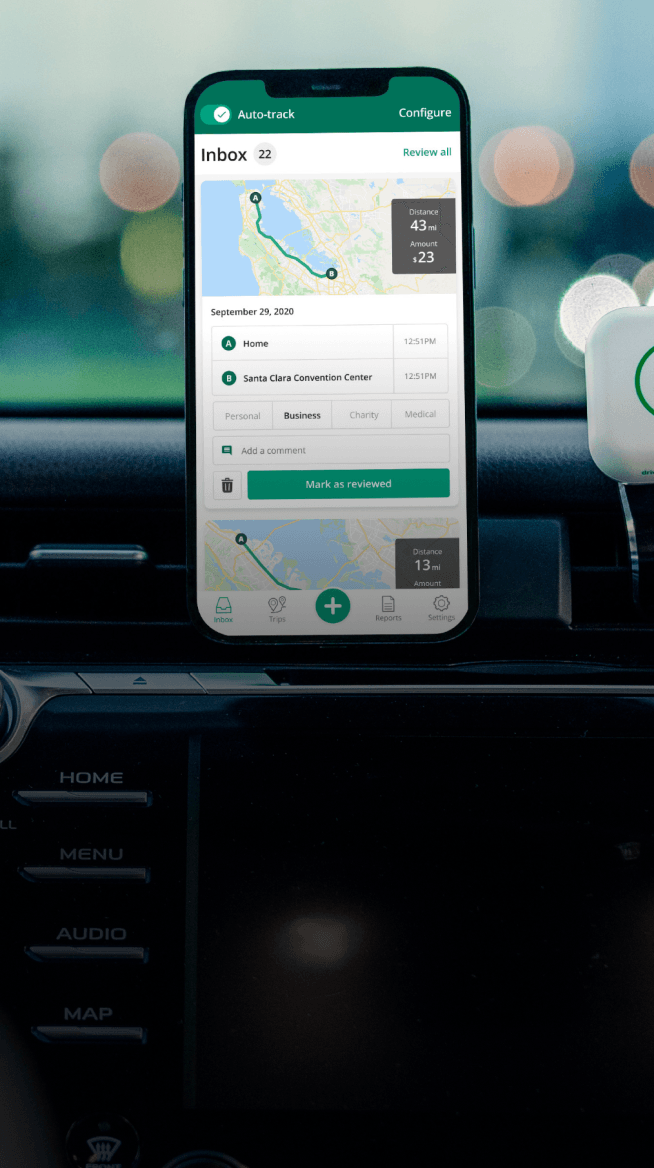
Automatic mileage tracking and HMRC-compliant reporting.
Get started for free Get started for freeHMRC mileage rates
The HMRC mileage rates for the 2024/2025 tax year are:
For cars and vans
- 45p for the first 10,000 business miles
- 25p for each business mile after the threshold of 10,000 miles
For motorcycles and bicycles
- 24p per business mile for motorcycles
- 20p per business mile for bicycles
The HMRC mileage rates have remained the same since 2011.
Expenses covered by the HMRC mileage rates
HMRC mileage rates cover the following vehicle expenses for your business miles:
- Fuel
- Servicing and repairs
- Maintenance
- Depreciation
- Insurance and road tax
Mileage rates do not cover:
- Road, bridge, tunnel tolls
- Parking fees
- Congestion charges
- Speeding or parking fines, other road offences
Mileage claim rules
For employees
If you use your personal vehicle for business-related driving, you can be reimbursed by your employer for your business miles. The reimbursement is also known as a Mileage Allowance Payment (MAP). The allowance covers all regular expenses for owning and maintaining your vehicle for its business usage. Mileage allowance payments are normally provided on a monthly basis and can be in the form of a per-mile rate or a lump sum for vehicle expenses. Some employers provide a combination of both.
In case your employer doesn’t reimburse you, you will be eligible for a mileage claim from HMRC for your business miles, also known as Mileage Allowance Relief, so long as you fulfil the requirements of what constitutes business-related driving and keep an HMRC-compliant mileage log. Continue to the “Mileage claim” section to find out more, and find more in-depth information about HMRC mileage claims in our Mileage Allowance Relief (MAR) article.
HMRC mileage rates for employees
Each year HMRC publishes advisory mileage rates that employers can use as a guide on the amount of allowance they should provide to employees. The current HMRC mileage rates are the same as mentioned above.
Note that if your reimbursement is higher than the advisory rates per mile, your mileage allowance will be taxed as income. If you receive the approved per-mile rate or lower, your mileage allowance is not taxed.
Records for your mileage claim
Your employer will require proof of your business-related driving in the form of mileage records in order to pay out mileage allowances. While they can decide what you should record in your mileage log, you can read further down about the general HMRC mileage records requirements.
Find out more about mileage allowance payments, if yours will be taxed and other rules you should be aware of in our article dedicated to mileage allowance for employees.
Car allowance
In the United Kingdom, a company car allowance is considered a monetary benefit, and your employer may opt to supply you with one. As an alternative to a business car scheme, an employee may be given a car allowance. The amount of your automobile allowance should be stated in your employment contract and is often paid monthly with your salary, while some employers choose to pay annually.
For self-employed individuals
HMRC outlines two methods for mileage claims for self-employed - the simplified expenses and the actual vehicle expenses methods.
Simplified expenses method
The simplified expenses method is based on a flat rate per mile that can be claimed for business-related mileage with one’s personal vehicle. The rates in question are the official HMRC mileage rates and they cover all costs related to owning and maintaining your vehicle for the business portion of its use.
If you use the simplified expenses method, you will be able to supplement your HMRC mileage claim with additional expenses on top of the per-mile rate, such as parking fees, car hire fees, the cost of travelling on other vehicles (bus tickets, for example) and more.
Actual vehicle costs claim
This HMRC mileage claim method allows you to claim all specific expenses connected with driving your personal vehicle for business purposes. You will need to keep receipts and invoices as proof for all eligible expenses you claim. These include:
- Fuel
- Vehicle insurance
- Repairs and maintenance
- Servicing
- Breakdown cover
- Parking
- License fees
While this method can be more labour intensive than the Simplified Expenses method, it is worth considering if your vehicle costs are higher due to high fuel consumption, high road tax etc.
If you use your vehicle for both business and personal driving, you cannot claim all vehicle expenses you’ve had during the year. You will have to determine the percentage of driving that was business-related throughout the year and claim actual vehicle expenses only for the percentage of work miles you’ve driven.
Claiming mileage from HMRC
You can claim Mileage Allowance Relief (MAR) at tax time from HMRC if your employer doesn’t reimburse you for your business-related vehicle expenses, or if you are a self-employed individual.
In order to claim MAR, you will need to keep compliant records of your mileage throughout the year as proof. Add up your mileage for the whole year and multiply by the HMRC mileage rate that applies to you - this will be your claim for mileage allowance relief. Read more about Mileage Allowance Relief.
Calculate your mileage allowance payments or relief with the calculator below.
How to keep compliant records for your HMRC mileage claim
In order to claim mileage from your employer or HMRC, you need documented proof substantiating your claim in the form of a mileage log.
While an employer may set their own requirements for what you should record in your mileage log, they will generally still ask for the records HMRC has set.
According to HMRC, your mileage log should include:
- The date of your journey
- If it is a personal or business-related journey
- The start and end addresses, including postcodes
- The total number of miles driven for the journey
An employer will likely ask for monthly mileage logs, in order to provide mileage reimbursement, while those claiming mileage from HMRC will need a year’s worth of data to claim mileage allowance relief at tax time.
Not located in the UK? Check out our other guides here:
- Mileage guide for the US (IRS mileage guide)
- Mileage guide for Australia (ATO mileage guide)
- Mileage guide for Canada (CRA mileage guide)
- Mileage guide for Denmark
- Mileage guide for Sweden
- Mileage guide for the Netherlands
FAQ
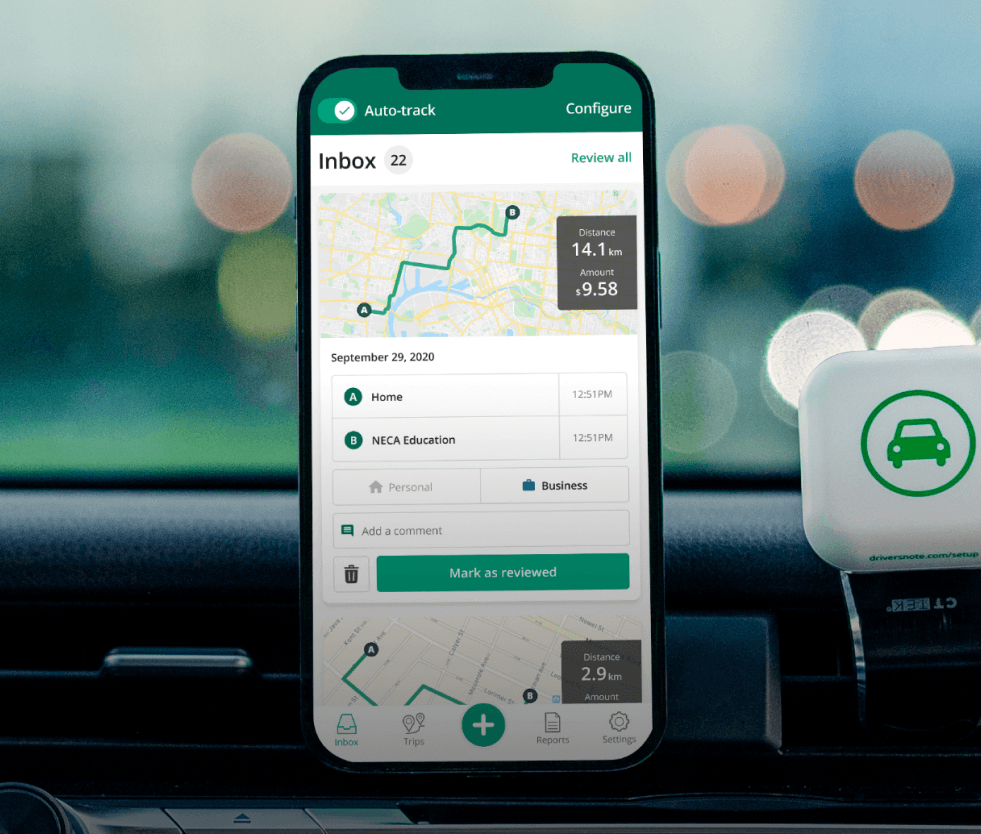
Tired of logging mileage by hand?
Effortless. HMRC-compliant. Liberating.
HMRC Mileage Guide
- For self-employed
- For employees
- HMRC mileage claim in 5 steps
- Self-employed mileage allowance records
- Car allowance for employees
- Salary sacrifice car scheme
- Mileage Allowance Relief
- HMRC mileage rate 2022
- HMRC mileage rates 2021